Orientations
This is a static version of a Jupyter notebook. Click to interact with the notebook:
Some example of caluations with quaternions
Import some modules. DefDAP can be downloaded from here: https://github.com/MechMicroMan/DefDAP. As of 28/02/2019 you will need to install from the develop branch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import defdap.ebsd as ebsd
from defdap.quat import Quat
%matplotlib inline
Calculate misorientation
eulers1 = [45., 30., 30.]
eulers2 = [45., 30., 50.]
eulers1 = np.array(eulers1) * np.pi / 180
eulers2 = np.array(eulers2) * np.pi / 180
q1 = Quat.fromEulerAngles(*eulers1)
q2 = Quat.fromEulerAngles(*eulers2)
misori = 2*np.arccos(q1.dot(q2))
print(round(misori*180/np.pi, 1), 'deg')
20.0 deg
q1.plotUnitCell(symGroup='cubic')
q2.plotUnitCell(symGroup='cubic')
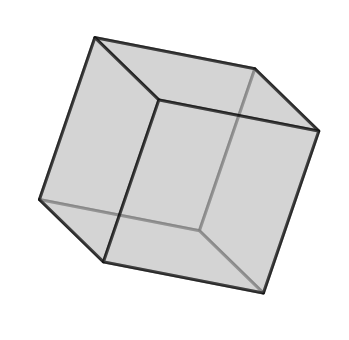
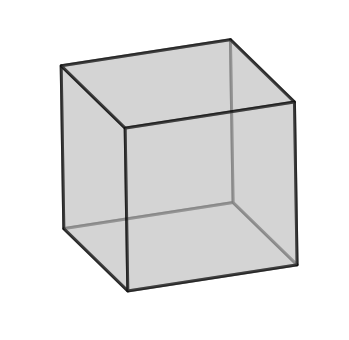
Calculate misorientation considering the symmetric equivalent orientations
eulers3 = [1., 112., 70.]
eulers3 = np.array(eulers3) * np.pi / 180
q3 = Quat.fromEulerAngles(*eulers3)
misori = 2*np.arccos(q2.dot(q3))
print(round(misori*180/np.pi, 1), 'deg')
89.5 deg
misori = 2*np.arccos(q2.misOri(q3, 'cubic'))
print(round(misori*180/np.pi, 1), 'deg')
0.6 deg
q2.plotUnitCell(symGroup='cubic')
q3.plotUnitCell(symGroup='cubic')
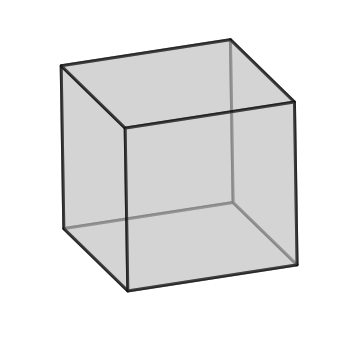
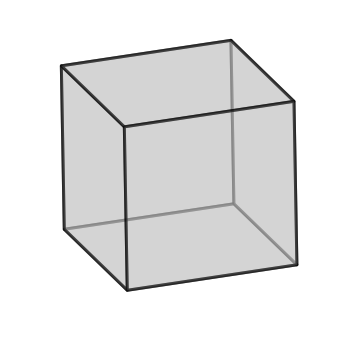
### Plot orientaions on an IPF
size = 200
quats = [q1, q2, q3]
colours = [1, 2, 3] # viridis scale so 1 is blue, 2 is greenish and 2 is yellow
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,3, figsize=(15,5))
Quat.plotIPF(quats, np.array([1,0,0]), "cubic", marker='o', s=size, c=colours, fig=fig, ax=axes[0])
Quat.plotIPF(quats, np.array([0,1,0]), "cubic", marker='o', s=size, c=colours, fig=fig, ax=axes[1])
Quat.plotIPF(quats, np.array([0,0,1]), "cubic", marker='o', s=size, c=colours, fig=fig, ax=axes[2])
plt.tight_layout()

Calculate symmetrically equivalent orientations
for symm in Quat.symEqv('cubic'):
symQuat = symm * q1
symEulers = symQuat.eulerAngles()*180/np.pi
print(round(symEulers[0], 1), '\t', round(symEulers[1], 1), '\t', round(symEulers[2], 1))
45.0 30.0 30.0
258.7 64.3 163.9
225.0 150.0 150.0
78.7 115.7 16.1
341.6 104.5 63.4
225.0 150.0 330.0
161.6 75.5 296.6
45.0 30.0 300.0
45.0 30.0 210.0
45.0 30.0 120.0
225.0 150.0 60.0
225.0 150.0 240.0
161.6 75.5 116.6
341.6 104.5 243.4
258.7 64.3 343.9
78.7 115.7 196.1
258.7 64.3 73.9
161.6 75.5 26.6
341.6 104.5 333.4
258.7 64.3 253.9
161.6 75.5 206.6
78.7 115.7 106.1
341.6 104.5 153.4
78.7 115.7 286.1
Calculate a possible twin orientation
An FFC annealing twin is a 60 deg rotation around a [111] crystal direction
axis = np.array([1.,1.,1.])
angle = np.pi/3
parentOri = q1
twinTransform = Quat.fromAxisAngle(axis, angle)
twinOri = twinTransform * parentOri
misori = 2 * np.arccos(parentOri.misOri(twinOri, 'cubic'))
misoriAxis = parentOri.misOriAxis(twinOri)
print(round(misori*180/np.pi, 1), 'deg')
print(misoriAxis)
60.0 deg
[0.60459979 0.60459979 0.60459979]
Mean orientaion
Demonstrate with some EBSD data
# Load in EBSD map, detect grains and calculate grain average orientations
# This data is available in defdap's github repo
ebsdFilePath = "./testDataEBSD"
crystalSymmetry = "cubic"
ebsdMap = ebsd.Map(ebsdFilePath, "cubic")
ebsdMap.loadSlipSystems("./cubic_fcc.txt")
ebsdMap.buildQuatArray()
ebsdMap.findBoundaries(boundDef=8)
ebsdMap.findGrains(minGrainSize=10)
ebsdMap.calcGrainAvOris()
Loaded EBSD data (dimensions: 359 x 243 pixels, step size: 0.12 um)
Finished building quaternion array
Finished finding grain boundaries
Finished finding grains
Finished calculating grain mean orientations
grain = ebsdMap[18]
size = 50
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,3, figsize=(15,5))
plot = grain.plotOriSpread(np.array([1,0,0]), fig=fig, ax=axes[0])
grain.plotRefOri(np.array([1,0,0]), marker='o', s=size, plot=plot)
plot = grain.plotOriSpread(np.array([0,1,0]), fig=fig, ax=axes[1])
grain.plotRefOri(np.array([0,1,0]), marker='o', s=size, plot=plot)
plot = grain.plotOriSpread(np.array([0,0,1]), fig=fig, ax=axes[2])
grain.plotRefOri(np.array([0,0,1]), marker='o', s=size, plot=plot)
<defdap.plotting.PolePlot at 0x22c6181cfd0>

Calculate components of slip direction in sample coordinates
Only for cubic crystals. For hexagonal crystals you have to transform to an orthonormal coordinate system in the crystal first (See pg 22 of Randle and Engle - Introduction to texture analysis)
slipDir = np.array([0,1,1])
slipDirQuat = Quat(0, slipDir[0], slipDir[1], slipDir[2])
slipDirSampleQuat = q1.conjugate * (slipDirQuat * q1)
slipDirSample = slipDirSampleQuat.quatCoef[1:4]
print(slipDirSample)
[-0.53033009 -0.1767767 1.29903811]
# or use method in the quat object
slipDirSample = q1.conjugate.transformVector(slipDir)
print(slipDirSample)
[-0.53033009 -0.1767767 1.29903811]
