Generating RVEs with particle distributions
Generalisation of particle-containing RVEs
In the dual-phase Ti simulation work in which we will ultimately develop a coupled crystal-plasticity/phase-field model, we have currently been using an RVE containing three $\alpha$-phase precipitate particles. To enable more general control over the morphology of the RVE, and, by extension, to support LightFORM researchers simulating other materials with multi-phase particles, we generalised the code to generate such RVEs. In particular, we made good use of the DAMASK Python package to implement a ParticleRVE class, which is parametrised according to one or more ParticleDistribution objects. In this code, a particle distribution is a set of ellipsoidal particles, which are characterised by their diameter lengths, major axis direction vector and major plane normal direction vector. The diameters (and other properties) can be specified in terms of normal distribution means and standard deviations. To generate a ParticleDistribution, we can specify two of the following three parameters: major_axis_length, number, target_volume_fraction, where the unspecified parameter will be calculated from the other two, and the volume of the RVE.
The code is included in our damask-parse Python package (in the particles module1), and will soon be integrated with MatFlow.
The following animation demonstrates the construction of a particle-RVE using the code below. In this code, we generate an RVE with five grains, seeded in random positions. Voxels are assigned according to a Voronoi tessellation. We define two particle distributions, one representing “alloying elements” (in this case, fewer larger particles whose minor axes lengths are 1/2 and 1/4 of their major axes lengths), and another representing “impurities” (in this case, these are smaller and more numerous spherical particles).
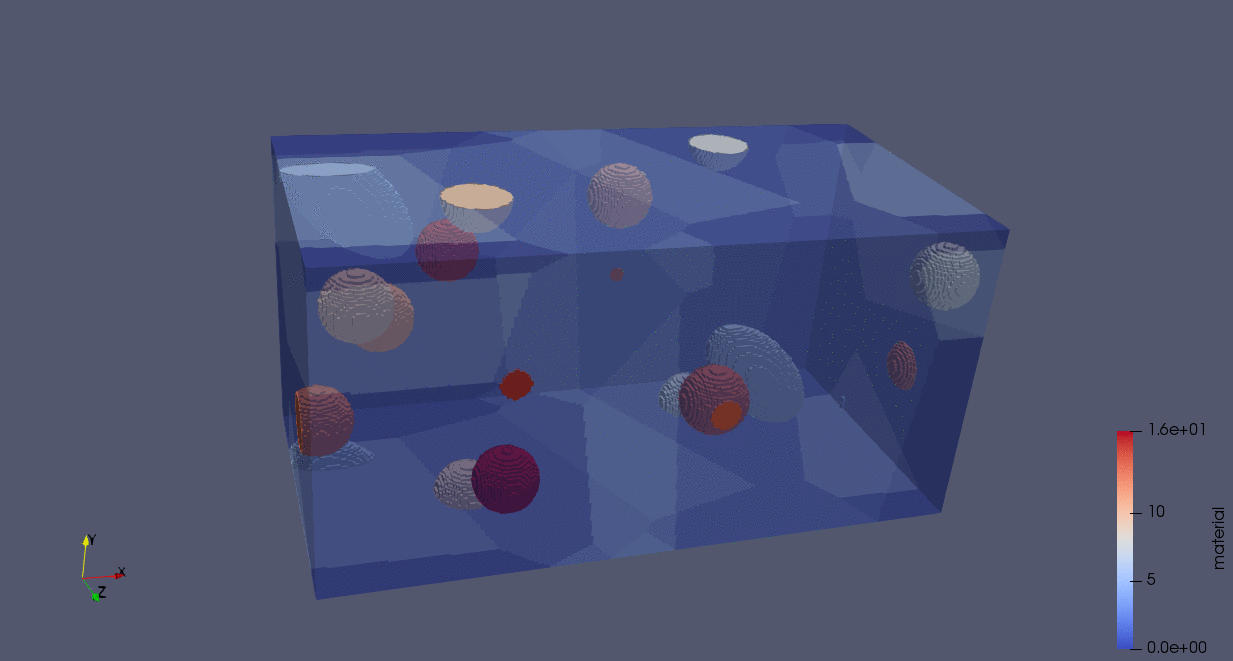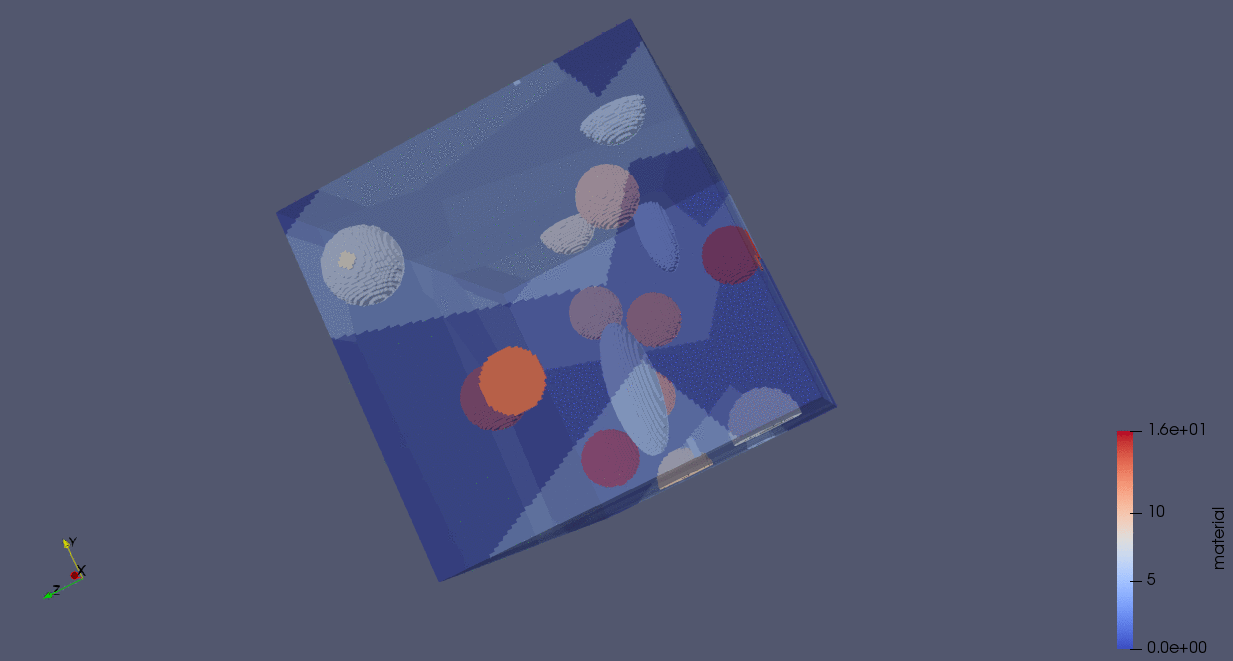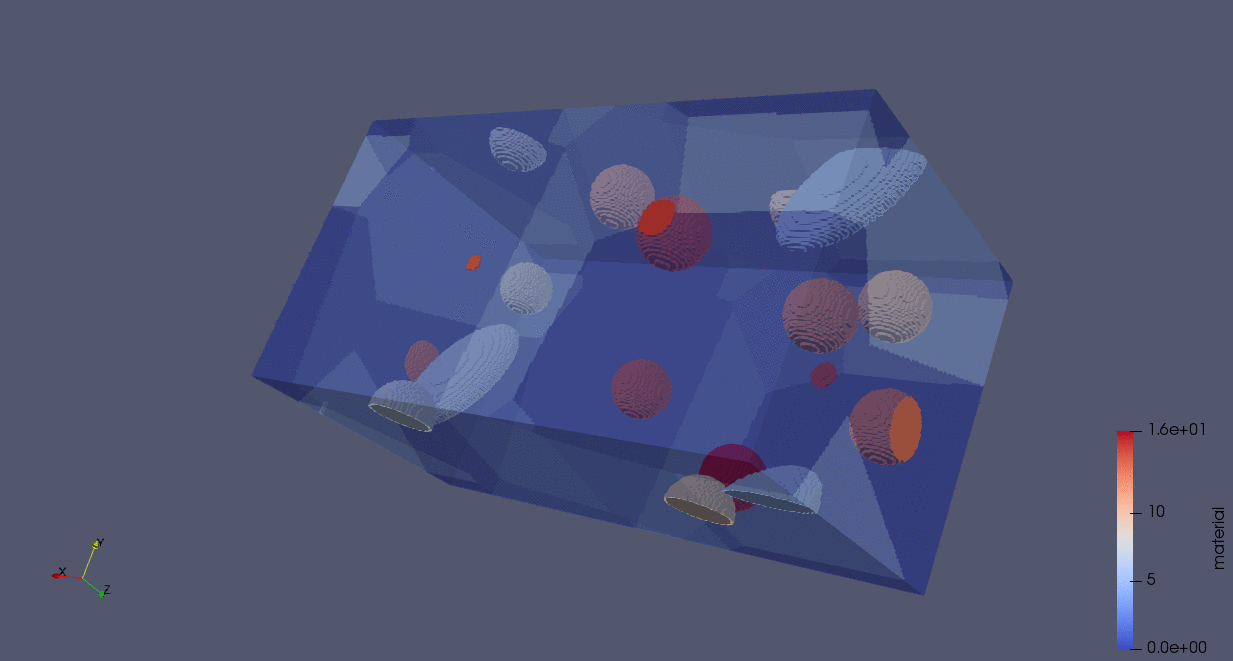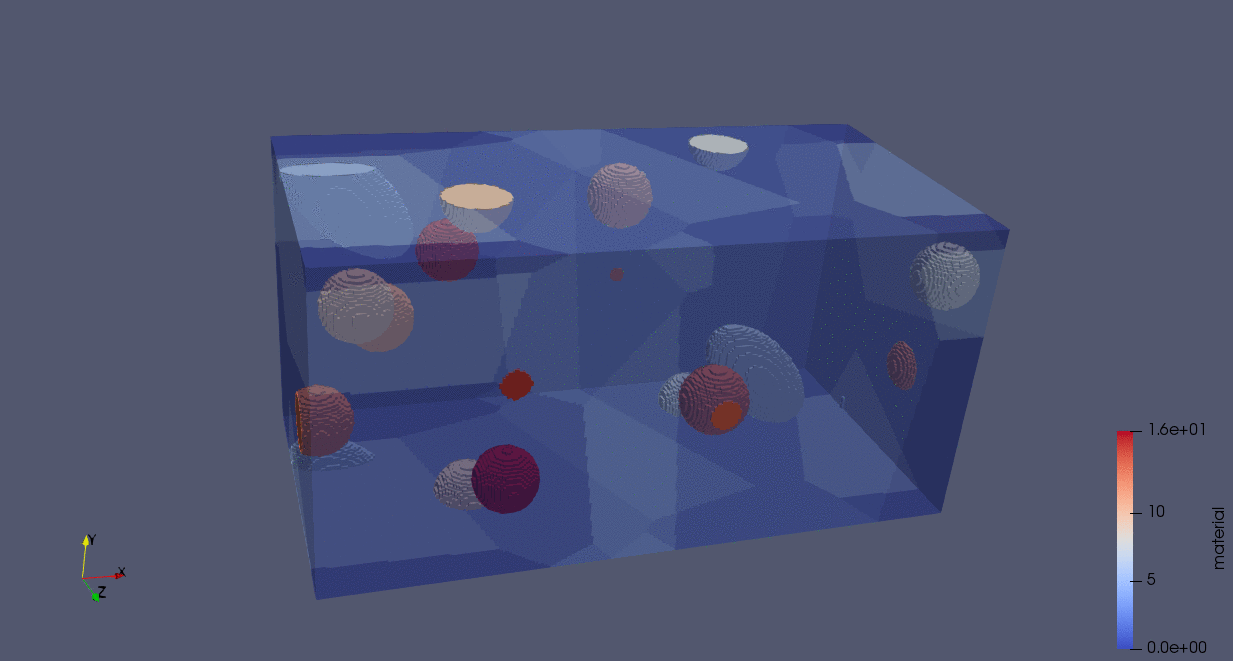
n_grains = 5
size = np.array([2, 1, 1])
cells = np.array([256, 128, 128])
seeds = size * np.random.rand(n_grains, 3)
pdist_1 = ParticleDistribution(
label='alloying_elements',
major_axis_length=0.5,
major_axis_length_stddev=0.005,
target_volume_fraction=0.01,
minor_axis_ratios=[0.5, 0.25],
major_axis_dir=[1, 1, 0],
)
pdist_2 = ParticleDistribution(
label='impurities',
major_axis_length=0.2,
major_axis_length_stddev=0.001,
number=10,
major_axis_dir=[1, 1, 0],
)
RVE = ParticleRVE.from_voronoi_tessellation(
size=size,
cells=cells,
seeds=seeds,
particle_distributions=[pdist_1, pdist_2],
)
RVE.save('RVE.vtr')
